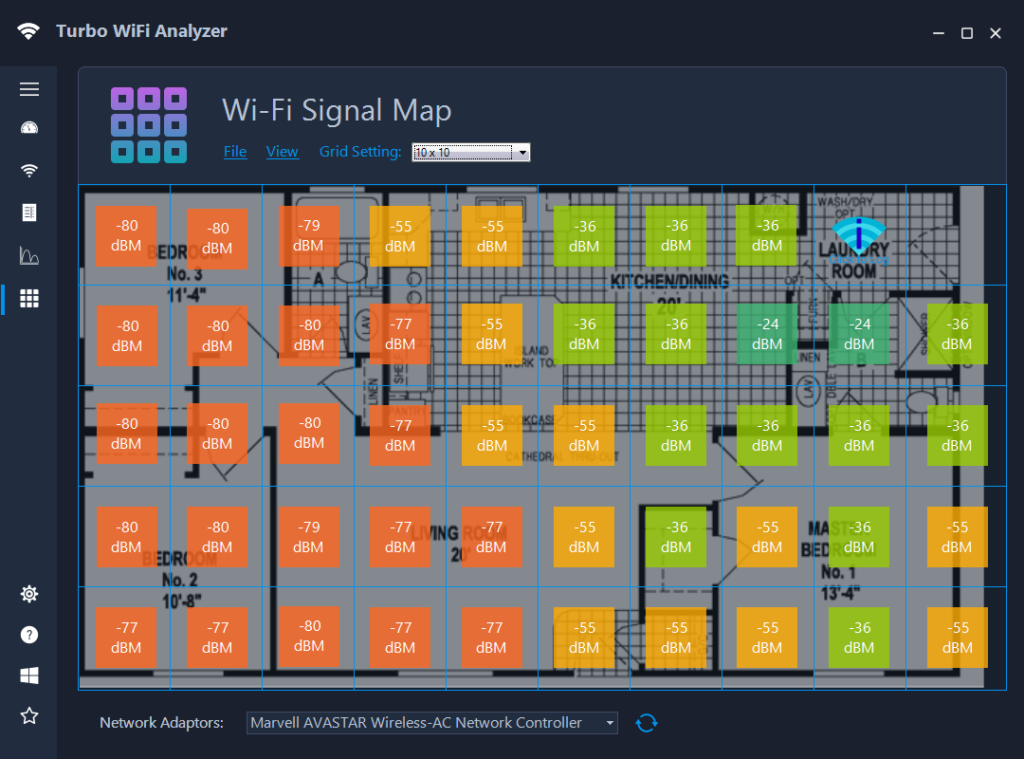
A signal heat map is a visual representation of the signal strength and coverage of your WiFi network in different areas of your home or office. It uses color-coding to indicate signal strength, with warmer colors like red and orange representing stronger signals, and cooler colors like blue and green representing weaker signals. By analyzing the heat map, you can identify areas with poor signal coverage, determine potential sources of interference, and make informed decisions to optimize your WiFi speed.
Table of Contents
ToggleCreating a Signal Heat Map
To create a signal heat map, you will need a WiFi analyzer tool that supports this feature. One such tool is the Turbo WiFi Analyzer app, which provides a user-friendly interface for generating signal heat maps. Start by opening the app and accessing the signal heat map feature. Walk around your space with your device while the app measures and records the signal strength at different locations. After gathering sufficient data, the app will generate a comprehensive heat map displaying signal strength variations across your environment.
Analyzing the Signal Heat Map
Once you have your signal heat map, it’s time to analyze the results. Look for areas with weak signal strength or dead spots, which are indicated by cooler colors on the map. These areas may be prone to signal interference or obstruction from physical barriers like walls or furniture. Identify the potential sources of interference, such as neighboring WiFi networks, electronic devices, or appliances, that may be causing signal degradation. Additionally, pay attention to areas where you typically use WiFi-intensive devices, such as your home office or entertainment center, as optimizing signal strength in these areas is crucial for optimal performance.
Optimizing WiFi Speed
Armed with the insights from your signal heat map, you can take steps to optimize your WiFi speed. Here are a few strategies to consider:
- Relocate Your Router: If your signal heat map reveals areas with weak coverage, consider moving your router to a more central location. This can help distribute the signal more evenly throughout your space and minimize signal loss due to physical barriers.
- Adjust Router Settings: Access your router’s settings and experiment with different configurations. You can try changing the channel to a less congested one, adjusting the transmit power, or optimizing other advanced settings based on the insights gained from the signal heat map.
- Use WiFi Extenders or Mesh Systems: In areas with persistent weak signal coverage, consider using WiFi extenders or mesh systems to amplify and extend the WiFi signal. These devices can help eliminate dead spots and provide a more reliable connection in larger spaces.
- Minimize Interference: Identify and mitigate sources of interference by relocating electronic devices, reducing the number of active devices, or using devices that operate on different frequency bands.